Umbilical cord formation
Around the second week of gestation, the extraembryonic body cavity disappears and the amniotic membrane wraps the allantois, the urothelial vessels, the yolk sac and its surrounding extraembryonic mesoderm, and the blood vessels to form the umbilical cord. The left allantoic vein becomes the umbilical vein and the right allantoic vein degenerates. The two allantoic arteries become umbilical arteries, and the water-rich Wharton's jelly wraps around the umbilical vessels to protect them.
Functions of the umbilical cord
The umbilical cord connects the placenta to the fetus, facilitating the exchange of nutrients and waste. The umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus, connecting to the left portal vein in the fetal liver. The two umbilical arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta for gas and nutrient exchange
Umbilical cord cysts occur in about 0.4%-3.4% of early pregnancies. While most resolve spontaneously, some may persist throughout gestation.
Mechanism of umbilical cord cyst
The umbilical cord is enveloped by the amniotic membrane and contains Wharton’s jelly, umbilical blood vessels, and remnants of the yolk sac and allantois. Anomalies in the development of these structures can lead to conditions such as single umbilical artery, umbilical cord cysts, and other abnormalities.
The exact mechanism of occurrence is not fully understood. Some studies have hypothesized that umbilical cysts are associated with umbilical cord growth with spiral changes and physiologic intestinal hernia formation.
Umbilical cord cysts can be true and pseudocysts, of which pseudocysts are more common, for the huatong gum local edema or local metamorphosis of the formation of mucus in the cystic cavity, the surface of the epithelium is not covered, if its volume increases can be compression of the umbilical cord blood vessels and lead to fetal death, and umbilical cord blood vessels are mostly attached to the cysts, false umbilical cord cysts can cause fetal malformations or affect fetal development (eg, fetal growth restriction);
True cysts usually originate from the umbilical mesenteric duct or the ureteric duct. Since true cysts often occur at the fetal end of the umbilical cord, they are often combined with abnormalities of the genitourinary tract and the gastrointestinal tract, especially ureteric duct cysts combined with umbilical bulge and open umbilical ureter.
True cyst (med.) | False cyst (med.) | |
| Types | Uncommon | Common |
Often combined with umbilical dilatation, open umbilical ureters | Only thickening of the umbilical cord and cystic changes are manifested | |
Chromosomal abnormality | Uncommon | False cyst of the umbilical cord detected in mid to late life are mostly associated with chromosomal abnormalities, mostly trisomy 18. |
Genesis | Originating from the remains of the urinary bladder, yolk sac and mesenteric tissue | Associated with degeneration of the cord, edema, and fluid collection. |
Size | Mostly smaller | Varying sizes |
Secretory function | The wall of the capsule is lined with epithelial cells that have a secretory function | No epithelial cell lining |
Umbilical cord cysts appear on ultrasound as round, spindle-shaped, or irregular anechoic areas attached to the umbilical cord, with well-defined, thin walls and excellent internal sound transmission. They may move with the umbilical cord. Color Doppler typically shows no blood flow within the cyst, with umbilical blood flow passing adjacent to or through the cyst.
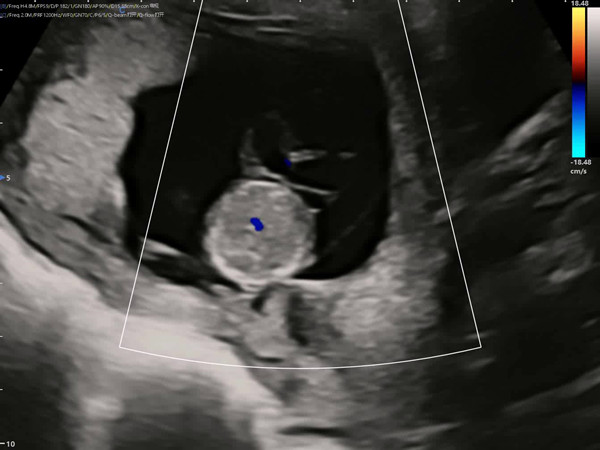
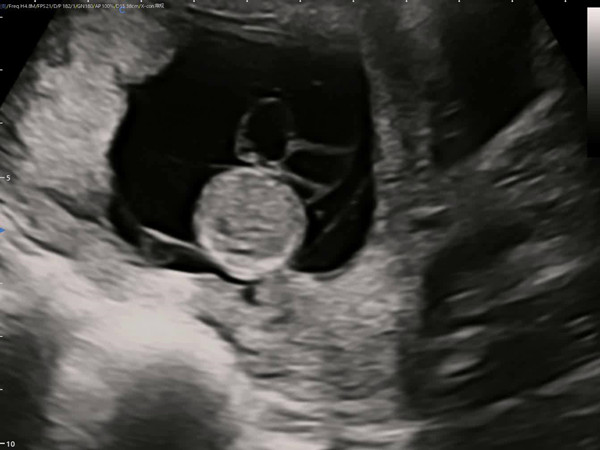
Fetal umbilical cord cysts need to be carefully differentiated from other conditions, such as umbilical hematoma, omphalocele, and umbilical cord edema.
Umbilical hematoma, often occurring in shorter cords, appears as a bulging, echogenic mass within the cord. Omphalocele presents as a sac-like protrusion at the umbilicus, with fetal organs visible within the sac on ultrasound. Umbilical cord edema, characterized by thickening of the cord, is a result of Wharton’s jelly edema.
Contact Us
Copyright © CHISON Medical Technologies Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved | Privacy and terms of use
Products: Vascular Ultrasound Machine MSK Ultrasound Machine Portable Ultrasound Device Portable Ultrasound Machine for Sale Portable Ultrasound Machine For Pregnancy Handheld Ultrasound For Pregnancy Handheld Veterinary Ultrasound Veterinary Ultrasound Machine Portable Vascular Ultrasound Livestock Ultrasound Machine

CHISON respects your privacy. We use cookies to make our site more personal and enhance your experience. Read our Private Policy to learn more about cookies and how to manage them. You agree to our use of these technologies when you visit our site.

We appreciate your feedback
We sincerely invite you to participate in our survey for helping us to improve our digital market.
*1.How fast does the website load?
*2.Does the products displayed on the website interest you?
*3.How easy is it for you to find the information you need?
4.What information or service do you suggest we can offer?


THANKS
Thank you for sharing your thoughts with us. We’re highly appreciated your every feedback.

Sorry!

THANKS
Thank you for sharing your thoughts with us. We’re highly appreciated your every feedback.